Note: This article is for general information only and no medical treatment is claimed. Always consult your doctor for more information and make appropriate changes as per his advice.

Introduction:
The human respiratory system plays a vital role in our overall well-being, allowing us to breathe and receive oxygen. However, it is susceptible to various diseases that can compromise its function and affect our quality of life. In this blog, we will delve into the world of lung diseases, exploring their causes, symptoms, and available treatment options.
What is pulmonary interstitial disease?

The term interstitial lung disease (ILD) refers to a collection of more than 200 disorders that damage and scar the lungs. The tissues between your lungs’ tiny air sacs (alveoli) and the blood arteries surrounding them are harmed by ILD. You will find it more difficult as a result to transfer oxygen from your lungs to your body.
Diffuse parenchymal lung disease (DPLD) is another name for interstitial lung disease.
What types of lung conditions are interstitial?
More than 200 different interstitial lung disorders exist. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis is the most prevalent, followed by conditions brought on by occupational exposures or connective tissue illnesses. Other instances include:
- Asbestosis.
- Silicosis.
- pneumonitis from radiation.
- pneumonia with interstitial etiology.
What signs or symptoms are there for interstitial lung disease?
The following are typical signs of interstitial lung disease:
- Dyspnea is shortness of breath that gets worse with activity or effort.
- cough that is dry.
- Fatigue.
- Anxiety in the chest.
Typically, symptoms are minor at first but worsen over months or years. Depending on the ILD’s underlying etiology, you can experience other symptoms.
Which drugs and therapies are utilized to treat interstitial lung disease?
1 .Corticosteroids
Prednisone-type medications can aid in reducing inflammation.
2 .Cytotoxic and anti-fibrotic medications.
These drugs can reduce lung scarring. Azathioprine, cyclophosphamide, pirfenidone, and nintedanib are a few of them.
3. Biologic medicines.

There are times when autoimmune conditions and other causes of ILD are treated with drugs like rituximab.
4 . oxygen treatment.

If your blood or tissues aren’t getting enough oxygen, your doctor will prescribe more of it. It enters your nose through a mask or tube.
5.Therapy for GERD.
Because gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) can exacerbate ILD, your doctor could advise taking medication to lower stomach acid.
What side effects might interstitial lung disease cause?
Life-threatening complications can result from interstitial lung disease in extreme situations, including:
- Pulmonary hypertension is high blood pressure in the lungs.
- lung collapse (pneumothorax).
- infected lungs.
- respiratory malfunction.
- lung tumors.
Asthma

Asthma is a long-term inflammatory condition that damages the airways and impairs breathing. Allergens, physical activity, cold weather, and respiratory illnesses are typical triggers. Wheezing, coughing, chest tightness, and shortness of breath are all signs of asthma. Medications including bronchodilators and anti-inflammatory medicines are frequently used in treatment, along with lifestyle changes to control triggers.
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)
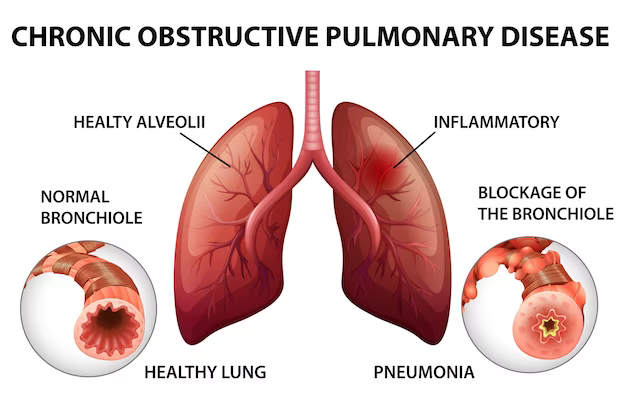
COPD is a progressive lung disease primarily caused by long-term exposure to irritants such as tobacco smoke and air pollution. It encompasses conditions like chronic bronchitis and emphysema. Symptoms include chronic cough, excessive mucus production, breathlessness, and reduced exercise tolerance. Treatment involves bronchodilators, inhaled corticosteroids, pulmonary rehabilitation, and smoking cessation.
Pneumonia:
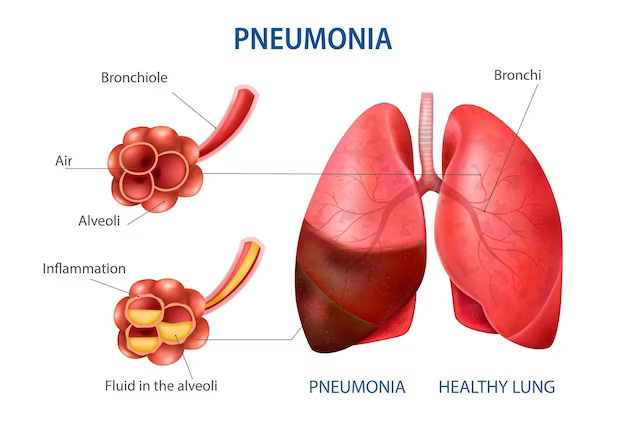
Pneumonia is an infection that inflames the air sacs in one or both lungs, leading to symptoms such as cough, fever, chest pain, and difficulty breathing. It can be caused by bacteria, viruses, fungi, or parasites. Treatment depends on the underlying cause and severity of the infection and may involve antibiotics, antiviral drugs, rest, and supportive care.
Pulmonary Fibrosis:
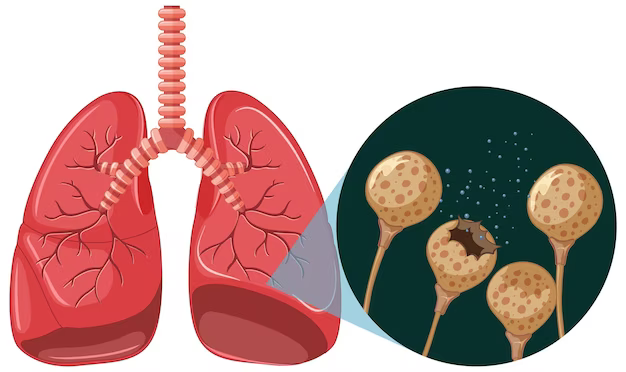
Pulmonary fibrosis is a chronic lung disease characterized by scarring of the lung tissue. It can be caused by factors like exposure to environmental toxins, certain medications, and autoimmune diseases. Symptoms include progressive shortness of breath, dry cough, fatigue, and unexplained weight loss. Treatment options may include medications to slow the progression of fibrosis, oxygen therapy, pulmonary rehabilitation, and lung transplantation in severe cases.
Lung Cancer:
Lung cancer is a malignant tumor that starts in the cells of the lungs. It is primarily caused by tobacco smoke but can also be linked to exposure to radon gas, asbestos, and other carcinogens. Symptoms may include persistent cough, chest pain, weight loss, and difficulty breathing. Treatment options include surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, targeted therapy, and immunotherapy, depending on the stage and type of lung cancer.
Conclusion:
Lung diseases can significantly impact an individual’s respiratory function and overall well-being. Early detection, proper management, and lifestyle changes can greatly improve outcomes for those affected. If you experience any persistent respiratory symptoms, it is crucial to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment. Remember, taking care of your lungs is essential for maintaining good health and a high quality of life.

