Note:
This article is for general information only and no medical treatment is claimed. Always consult your doctor for more information and make appropriate changes as per his advice.
Introduction:
Knee pain is a common complaint that affects people of all ages and lifestyles. Whether it stems from an injury, overuse, or underlying conditions, knee pain can significantly impact daily activities and quality of life. In this blog, we will delve into the causes, treatment options, and preventive measures for knee pain to help you better understand and manage this discomforting issue.
Causes of Knee Pain:
Injuries Traumatic incidents such as ligament tears (ACL, MCL), meniscus tears, fractures, or dislocation can lead to acute knee pain.
1.Overuse :
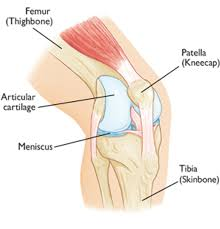
Repetitive strain on the knees, often seen in athletes or individuals who engage in excessive physical activities, can cause conditions like patellar tendinitis or runner’s knee.
2.Osteoarthritis:
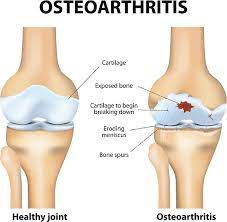
The most prevalent form of arthritis, osteoarthritis, occurs when the protective cartilage cushioning the knee joint wears down, resulting in pain, stiffness, and inflammation.
3.Rheumatoid Arthritis:
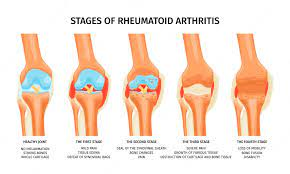
An autoimmune disease that causes chronic inflammation in the joints, including the knees.
4.Bursitis:
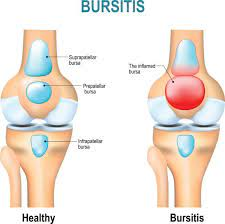
Inflammation of the bursae, small fluid-filled sacs that cushion the knee joint, usually caused by repetitive kneeling or pressure on the knee.
5.Tendonitis:
Inflammation of the tendons around the knee due to injury or overuse.
6.Other factors:
Obesity, age-related wear and tear, improper posture, and certain medical conditions can contribute to knee pain.
Treatment Options:
Rest and Ice:

Resting the affected knee and applying ice packs can help reduce pain and inflammation.
Medications:

Over-the-counter pain relievers (e.g., acetaminophen, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) can provide temporary relief. In severe cases, prescription medications may be necessary.
Physical Therapy:

Targeted exercises can help strengthen the knee muscles, improve flexibility, and reduce pain.
Knee Braces or Supports:
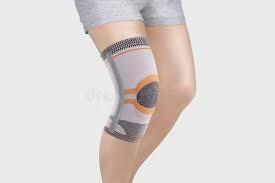
Wearing a brace or using supportive devices can provide stability and relieve pressure on the knee joint.
Injections:
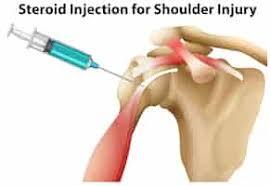
Corticosteroid injections may be administered to reduce inflammation and pain. Hyaluronic acid injections can provide lubrication to the joint.
Surgical Interventions:
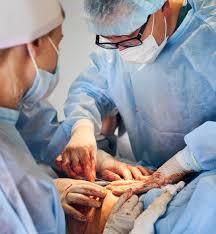
In cases of severe damage or persistent pain, surgical procedures such as arthroscopy, partial knee replacement, or total knee replacement may be recommended.
Prevention Tips:
Maintain a healthy weight to reduce stress on the knees.
1.Engage in regular low-impact exercises like swimming or cycling to strengthen the muscles supporting the knees.

2. Warm up before physical activities and stretch afterward to improve flexibility and reduce the risk of injury.

3.Use proper footwear and supportive inserts if needed.

4.Avoid prolonged kneeling or activities that put excessive strain on the knees.
5.Practice good posture and body mechanics to minimize stress on the joints.
6.Listen to your body and give yourself time to rest and recover after intense activities.

Conclusion:
Knee pain can significantly affect our daily lives, but with the right knowledge and proactive measures, it can be managed effectively. Identifying the underlying causes, seeking appropriate treatment options, and adopting preventive strategies will play a crucial role in alleviating knee pain and promoting overall joint health. Remember, if you’re experiencing persistent or worsening knee pain, it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional for a comprehensive evaluation and personalized treatment plan. Take care of your knees, and they will support you for years to come.

