Note: This article is for general information only and does not claim any medical treatment. Always consult your doctor for more information and make appropriate changes as per his advice.

Introduction
Psoriasis is a chronic skin condition that affects millions of people worldwide. While it may not be a life-threatening disease, its physical and emotional impact on those who suffer from it can be significant. This blog aims to provide you with a comprehensive overview of psoriasis, including its causes, symptoms, and various treatment options available to manage this condition effectively.
What Is Psoriasis?

Psoriasis is an autoimmune skin disorder characterized by the rapid buildup of skin cells.
Normally, skin cells are replaced every 3 to 4 weeks, but in individuals with psoriasis,
this process takes just a few days. As a result, skin cells accumulate and form thick,
scaly patches on the skin’s surface. These patches can appear anywhere on the body but
are most commonly found on the elbows, knees, scalp, and lower back.
Causes of Psoriasis

The exact cause of psoriasis remains unclear, but it is believed to be a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Some of the known factors that may trigger or exacerbate psoriasis include:
Genetics:
Psoriasis often runs in families. If you have a family member with psoriasis, you may be
at a higher risk of developing it yourself.
Immune System Dysfunction:
Psoriasis is considered an autoimmune disease, where the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy skin cells.
Environmental Triggers:
Certain environmental factors, such as infections, stress, or injuries to the
skin, can trigger psoriasis flare-ups.
Medications:
Some medications, such as lithium, beta-blockers, and certain antimalarial drugs,
can trigger or worsen psoriasis.
Symptoms of Psoriasis –

Psoriasis can manifest in several ways, and its symptoms can vary from person to person. The most common symptoms include:
Red, Inflamed Skin:
Affected areas of the skin often appear red, swollen, and covered with silvery-white scales.
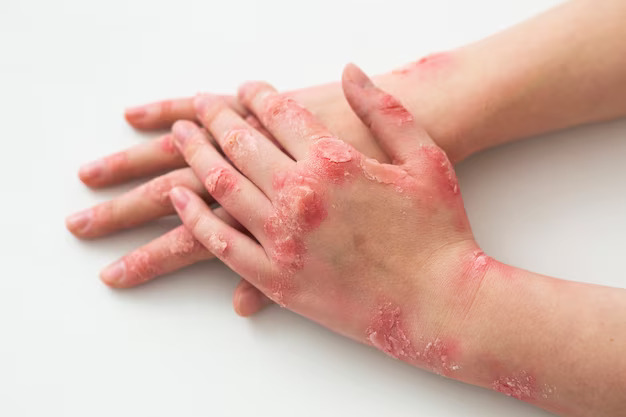

Itching and Discomfort:
Psoriasis can be itchy and uncomfortable, leading to scratching and potential skin damage.

Thickened Nails:
Psoriasis can affect the nails, causing them to become thickened, pitted, or discolored.

Joint Pain:
In some cases, psoriasis can also affect the joints, leading to a condition known as psoriatic arthritis, which can be painful and debilitating.
Treatment Options for Psoriasis –
While there is no cure for psoriasis, there are several treatment options available to help manage its symptoms and improve the quality of life for those affected. The choice of treatment depends on the severity of the condition and individual preferences. Here are some common treatment options:
Topical Treatments:
These include creams, ointments, and shampoos containing corticosteroids, vitamin D analogs, or tar. They are applied directly to the affected skin or scalp.
Phototherapy (Light Therapy):
Exposure to ultraviolet (UV) light under controlled conditions can help reduce psoriasis symptoms.

Systemic Medications:
In more severe cases, oral or injected medications that affect the immune system may be prescribed. These include biologics, methotrexate, and cyclosporine

Lifestyle Changes:
Managing stress, maintaining a healthy weight, and avoiding triggers such as smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can help reduce psoriasis flare-ups.

Natural Remedies:
Some individuals find relief from psoriasis symptoms through natural remedies like aloe vera, fish oil supplements, or bathing in Dead Sea salt.
Conclusion
Psoriasis is a chronic (long-lasting) disease in which the immune system becomes overactive,
causing skin cells to multiply too quickly. Patches of skin become scaly and inflamed, most
often on the scalp, elbows, or knees, but other parts of the body can be affected as well

